Image Guided Biopsy
Image-Guided Biopsy:
Precision Diagnosis with Minimal Invasion
When a suspicious area is found inside the body, determining its nature is a critical step toward effective treatment. An image-guided biopsy is a state-of-the-art, minimally invasive procedure that allows physicians to accurately obtain tissue samples for diagnosis without the need for major surgery. This guide will help you understand the procedure, its benefits, and what to expect.
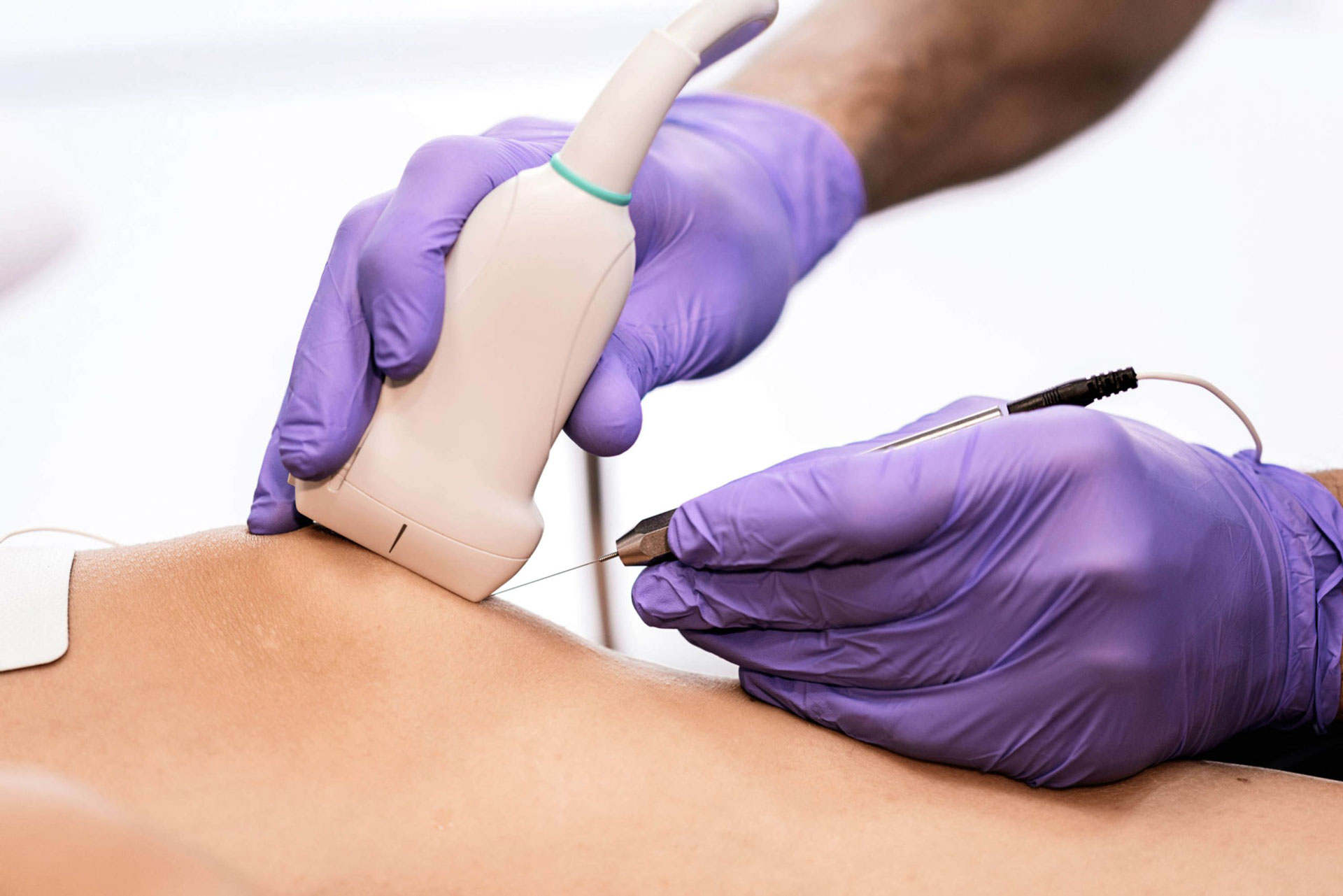
What is an Image-Guided Biopsy?
An image-guided biopsy is a advanced diagnostic technique where physicians use live imaging modalities—including Computed Tomography (CT), ultrasound, or fluoroscopy (a type of X-ray)—as a map to navigate a biopsy needle to a precise location within the body. This allows for the safe and accurate retrieval of tissue samples from organs, masses, or other suspicious areas for laboratory analysis.
Primary Biopsy Techniques
The specific biopsy method used is tailored to your individual needs, based on the location and nature of the area being examined. The two primary techniques are:
Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
Utilizes a specialized hollow needle to obtain a small core of tissue, preserving its architectural structure. This is often the preferred method for diagnosing tumors.
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
Employs a very thin gauge needle to suction out a sample of cells or fluid. It is often used for cystic lesions or easily accessible masses.
Advantages Over Surgical Biopsy
Image-guided biopsy is a significant advancement over traditional surgical methods, offering key benefits that enhance patient comfort and outcomes. The primary advantages include:
Minimally Invasive Procedure
Eliminates the need for large incisions and general anesthesia, which significantly reduces patient discomfort and recovery time.
Enhanced
Accuracy
Real-time imaging ensures the needle targets the exact area of concern, improving diagnostic yield.
Reduced Complications
The procedure is outpatient-based and carries a lower overall risk profile compared to open surgical biopsy.
Considering the Risks
Image-guided biopsy is a safe procedure, but no medical intervention is entirely without risk. The most common considerations include:
- Bleeding or hematoma at the biopsy site
- Infection
- Rarely, injury to adjacent structures
Your radiologist will discuss these risks with you in detail and ensure the benefits outweigh any potential complications.