Cancers
Understanding Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment with Interventional Radiology
This guide explains how interventional radiology helps diagnose and treat cancer—using precise imaging techniques for biopsies and minimally invasive tumor treatments.
What is Cancer?
How Abnormal Cells Form Tumors
Cancer develops when cells in the body become damaged and start growing out of control. Instead of following the normal cycle of growth and replacement, these abnormal cells keep multiplying and form clusters called tumors. Healthy cells grow in an orderly way and stay where they belong, but cancer cells grow uncontrollably and can invade nearby tissues. Some may even break away and spread to other parts of the body, making treatment more challenging.
Interventional Radiology in Cancer Treatment
Advances in medical technology have led to minimally invasive yet highly effective approaches for diagnosing and treating cancer—one of the most innovative being interventional radiology (IR).
IR combines advanced imaging techniques with precise procedures to diagnose cancer through Image-Guided Biopsies and deliver targeted treatments like Chemoembolisation and Thermal Ablation. These methods offer patients safer alternatives to traditional surgery, with faster recovery times and fewer complications.
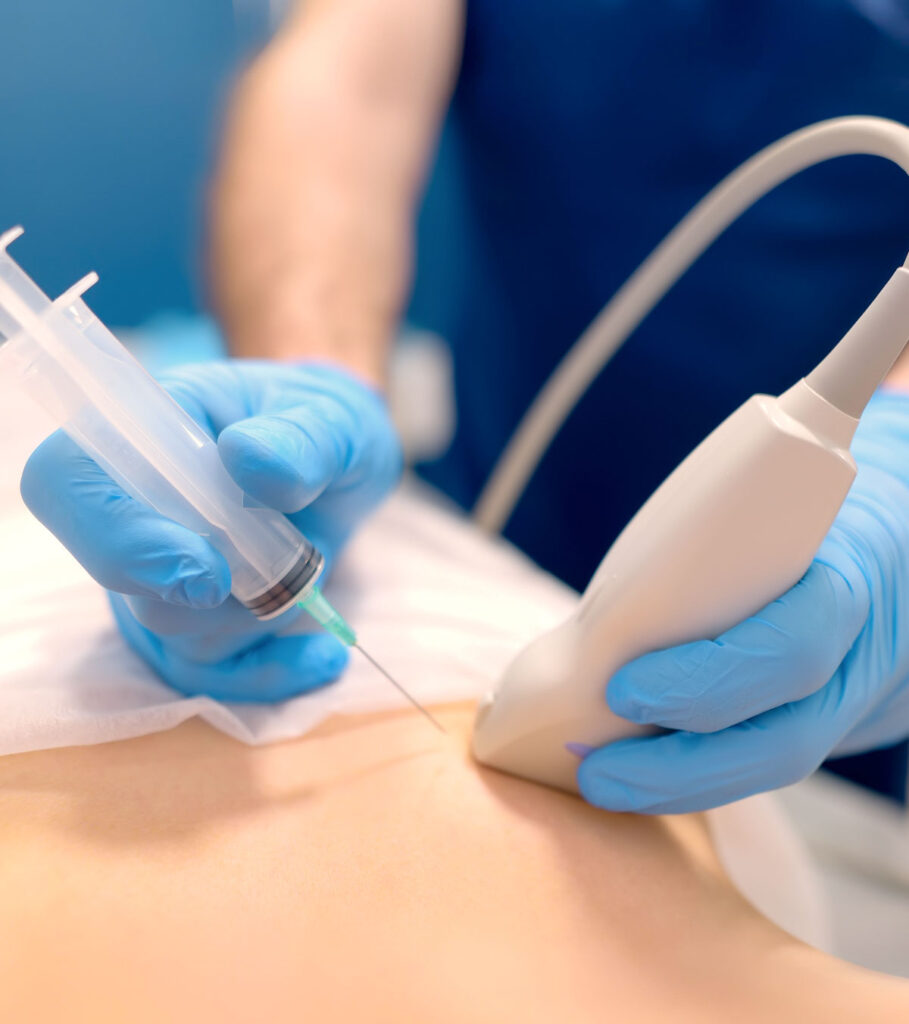
Image-Guided Biopsy: Overview, Benefits, and Risks
An Image-Guided Biopsy uses live ultrasound, CT, or MRI to carefully guide a needle and collect a tissue sample. This helps your doctor make an accurate diagnosis without surgery.
There are two main types: a Core Needle Biopsy (removes a small tissue sample) and Fine Needle Aspiration (collects fluid or cells).
This procedure is Minimally Invasive, precisely targeted, and usually requires only local anesthesia. Recovery is typically quick, with most people returning home the same day.
While generally very safe, there is a small risk of bleeding or infection. Your doctor will discuss all details with you beforehand.
Advanced Minimally
Invasive Cancer Treatments
Modern medicine offers precise, less invasive options for treating cancer. Learn about two advanced procedures—Chemoembolisation and Microwave Ablation—which directly target tumours while protecting healthy tissue. These treatments can lead to quicker recovery times and are designed to minimise discomfort during and after the process.
Chemoembolisation: Targeted Liver Cancer Therapy
Chemoembolisation is a minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer that works in two precise steps:
First, using live X-ray imaging, a thin tube is guided directly to the blood vessels feeding the tumor.
Then, chemotherapy medicine is delivered right to the tumor, followed by tiny particles that block its blood supply. This traps the medication inside the tumor and cuts off its nutrients, while protecting your healthy liver tissue.
Microwave Ablation: Heating Away Tumors
Microwave ablation uses focused heat to destroy cancer cells. It can treat small tumors in the liver, lungs, kidneys, bones, or breast.
Using live ultrasound or CT imaging, a thin probe is guided directly into the tumor. The probe emits microwaves that create a small heat zone, destroying the cancer cells while protecting surrounding healthy tissue. The safest technique is chosen based on your specific condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes. Our minimally invasive treatments, which often utilize advanced technologies are proven to be highly effective. Compared to traditional open surgery, patients typically experience:
<ul>
<li>Significantly shorter recovery times</li>
<li>Less post-operative pain and scarring</li>
<li>A lower risk of infection</li>
</ul>
These benefits are consistently supported by recent clinical studies and contribute to better overall patient outcomes.
In most cases, yes. Following your consultation, our team will prepare and provide all the necessary medical documentation, including letters of medical necessity, to support your insurance claim. We recommend that you also contact your insurance provider to verify your specific plan's benefits for this procedure.
