Prostate
Understanding Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH is a common, non-cancerous prostate enlargement that affects urinary function in aging men. This guide covers the key symptoms to watch for, how doctors diagnose it, and a minimally invasive treatment option—explained in clear, simple terms.
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, commonly affecting men over 50. As the prostate grows, it can press against the urethra, leading to urinary difficulties. While BPH is not life-threatening, it can significantly impact quality of life.
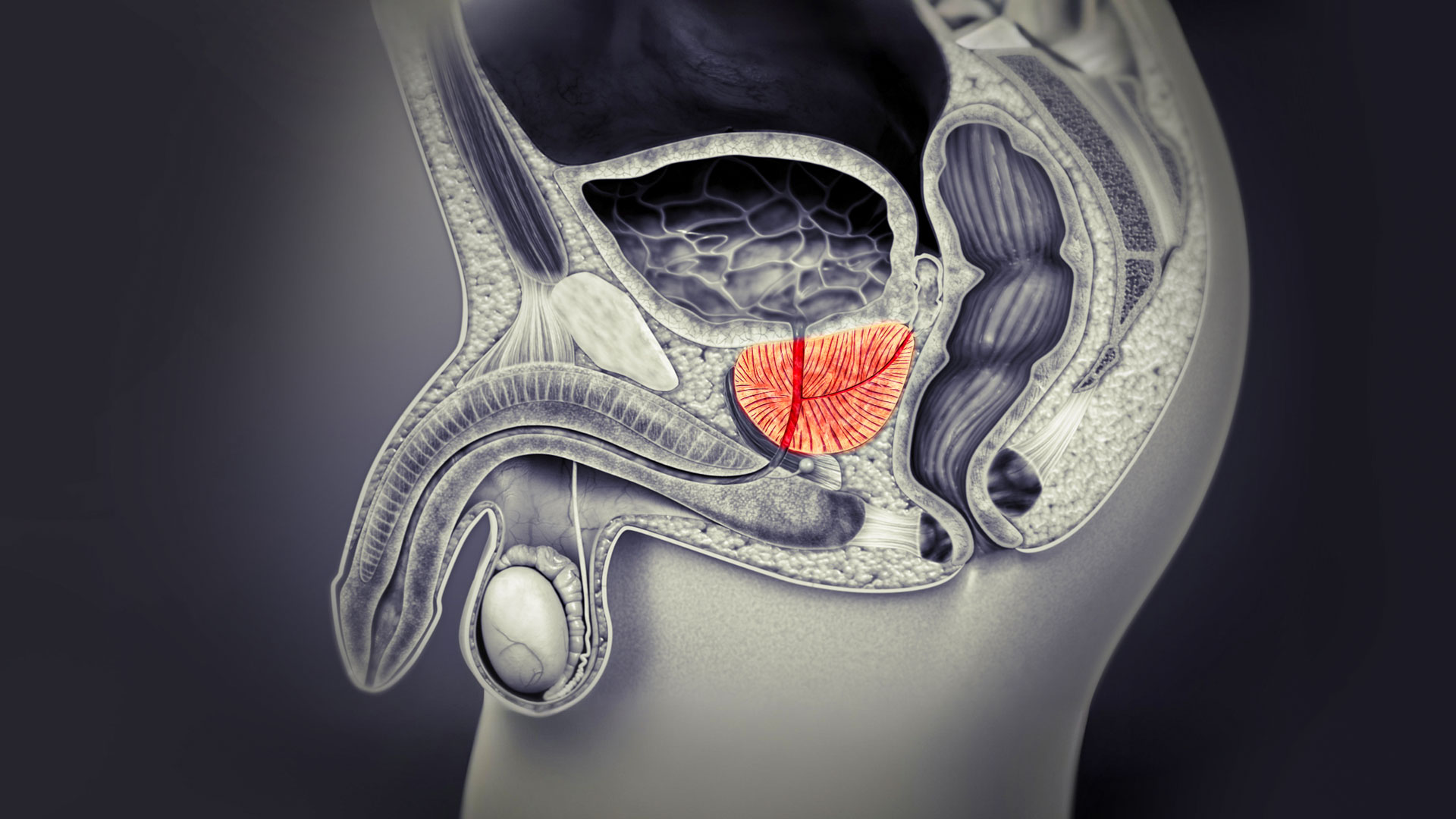
Symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
While BPH isn’t cancerous, recognising these warning signs is crucial for maintaining both comfort and long-term urinary health.
Pain or Burning during Urination
Discomfort or stinging sensation that may indicate infection
Frequent Urination
You need to urinate more often than usual, typically waking up 2+ times per night to go
Difficulty Starting Urination
You need to wait several seconds before urine begins to flow, even when your bladder feels full
Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Pink, red, or cola-colored urine that signals possible bleeding
Straining to Urinate
You have to push or bear down to get the urine stream started or maintain flow
Sudden, Strong Urges to Urinate
You get an intense feeling that comes on suddenly, sometimes leading to leaks if you don't reach a bathroom quickly
Feeling of Incomplete Emptying
After urinating, you still feel like some urine remains in your bladder
Dribbling after Urination
Urine continues to trickle out unexpectedly after you think you've finished
How Doctors Diagnose an Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
To confirm Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), doctors typically begin with a step-by-step approach:
Urine Tests
Checks for blood, infection, or signs of other urinary tract issues.
Imaging Tests
Ultrasound, Cystoscopy, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and Computed Tomography (CT).
Blood Tests
Prostate-Specific Antigen Elevated levels may indicate prostate enlargement or other conditions.

Advanced Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
At IR Clinic, we specialise in cutting-edge, minimally invasive treatments for BPH. One of our most effective solutions is Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)—a state-of-the-art procedure that offers significant relief with minimal downtime.
Minimally Invasive
No surgical incisions—just a small puncture site
Quick
Recovery
Most patients resume normal activities within 48 hours
High Success Rate
80-90% of men experience significant improvement
Preserves Function
Lower risk of sexual side effects compared to surgery
BPH doesn’t have to disrupt your life. With advanced treatments like PAE, relief is both achievable and long-lasting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Significantly shorter recovery times
- Less post-operative pain and scarring
- A lower risk of infection
